Connectors
Google BigQuery Connector
Google BigQuery is a great tool to use to store and analyze your video player data. Before you can send data to BigQuery, you'll need to configure a Connector.
Here are the things you'll need before you attempt to configure a Connector to Google BigQuery:
IMPORTANT
Please make sure that you have an appropriate Role attached to the service account that allows read/write access to BigQuery.
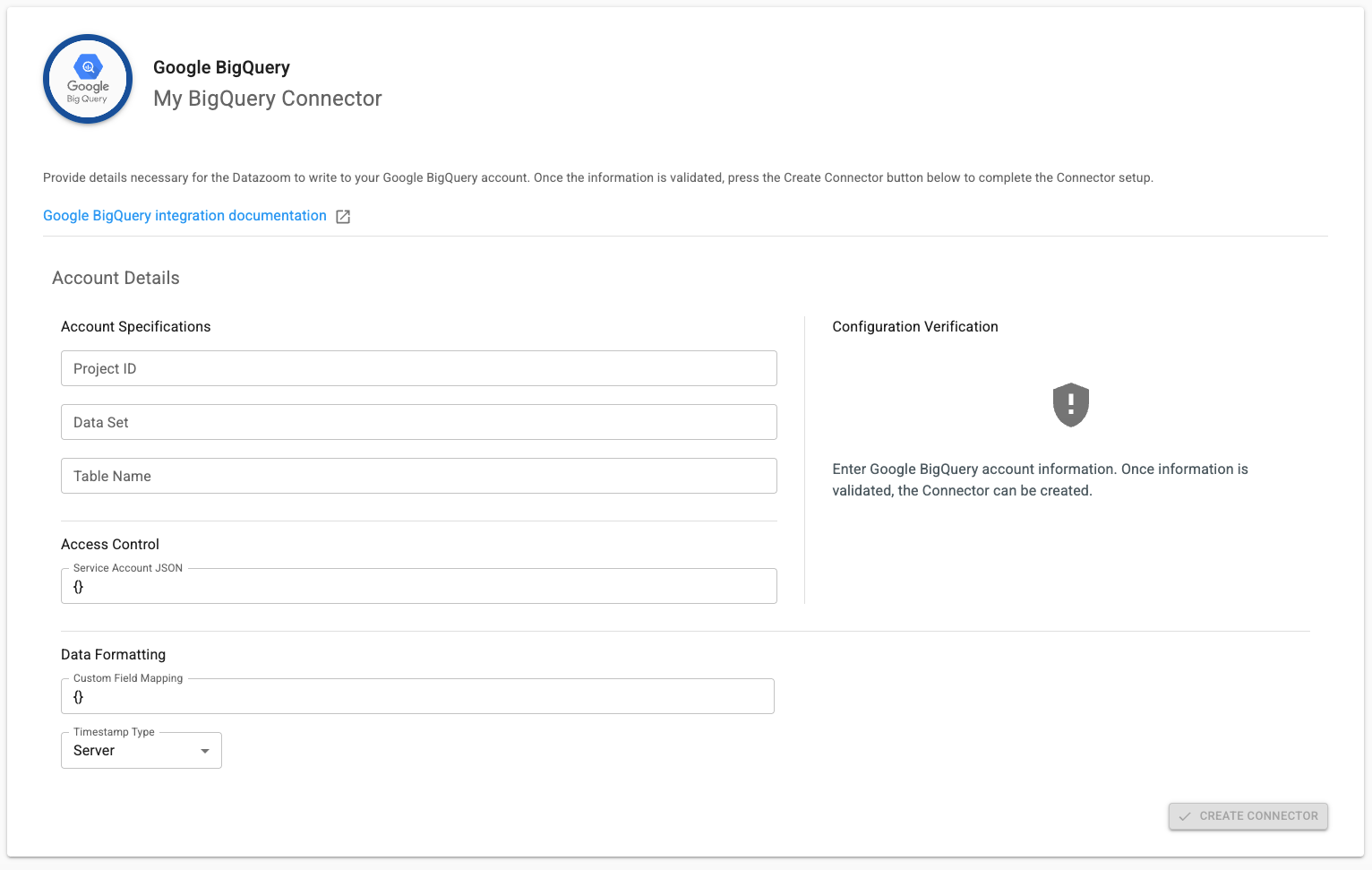
Project ID - Google BigQuery Project ID
Data Set - Google BigQuery Data Set
Table Name - Google BigQuery Table Name
Service Account JSON - as defined here: Service Account JSON
Custom Field Mapping - used to set your own field mapping (see below for details)
Timestamp Type
Server - The Datazoom platform timestamp (default setting)
Client - The uncorrected timestamp observed on the client
Client Corrected - The client timestamp corrected to align with NTP
Custom Field Mapping:
Datazoom automatically maps all data points contained in our Data Dictionaries and observed custom metadata to the BigQuery table configured above. The table must be configured using our Big Query Table Schema.
However, you can set your own field mapping for both your custom metadata and Datazoom data points. The example below shows how you can remap Datazoom data points event_id and streaming_protocol to your own names. It also shows how you can map your client-side custom metadata name isSubscribed to something meaningful in your data set.
{
"bq_table_mapping": {
"event_id": "my_event_id",
"streaming_protocol": "my_protocol",
"isSubscribed": "subscriber"
}
}
If you decide to use the remap feature, you must ensure that your BigQuery table is using the same name values and ensure your data types are accurate.
For example, if the mapping is set like above, then your BigQuery table schema would be:
[
{
"mode": "NULLABLE",
"name": "my_event_id",
"type": "STRING"
},
{
"mode": "NULLABLE",
"name": "my_protocol",
"type": "STRING"
},
{
"mode": "NULLABLE",
"name": "subscriber",
"type": "BOOLEAN"
}
]